
Table of contents [Show]
Computer Software Overview
- System Software
- Operating System
- Utility Software
- Device Driver
- Language Translator
- Compiler
- Interpreter
- Assembler
- Application Software
- Package Software
- Tailored Software
An operating system (OS) is a collection of software that manages computer hardware resources and provides common services for computer programs. The operating system is a vital component of the system software in a computer system.
An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware and controls the execution of all kinds of programs. An operating system is software that performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
Some popular Operating Systems include UNIX, Linux, Mac OS, Windows, etc.
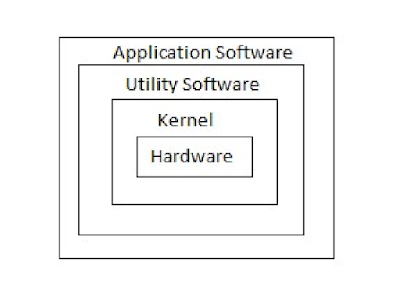
- OS Kernel: A main part of OS always remains in main memory during the running of a computer, called OS Kernel. It is the main controlling part of the OS which controls all running programs and the hardware resources. It is directly communicate with hardware as well as the upper layers.
- Utility Software: which are used as system management tools, also known as housekeeping work of OS. The main purpose of these tools is to make system up to date and efficient. Examples: Disk cleanup, Scan disk, disk defragmenter, device drivers, antivirus, file recovery, etc.
- Application Software: The software which are made on the request of user or organization in order to fulfil their requirements. Basic application software provided by windows OS are Notepad, WordPad, Paint and simple games.
- IO Management
- Command interpreter
- Data Management
- Memory Management
- Process Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Security
- Deadlock prevention (IMP)
- Virtual memory management:
- Paging: In paging, primary memory is portioned into fixed size called frame and the job is also portioned into same size is called page. Instead of loading the entire job at once, a few pages are loaded into the page-frame of memory.
- Swapping: In this technique, high-priority process is swapped in the main memory and low-priority process from main memory is swapped out. When the high-priority process is completed, the low-priority process is swapped in again.
- Batch processing OS:
- Multi-programming OS:
- Multitasking OS:
- Pre-emptive multitasking: It allows CPU time slice to each program. Windows 95, Windows NT use preemptive multitasking.
- Non pre-emptive multitasking: Each program can control the CPU for as long as it needs. If a program is not using the CPU, however, it can allow another program to use it temporarily. It is also called cooperative multitasking. Windows 3.x and Multi Finder use non-preemptive multitasking.
- Multiprocessing OS:
- Multithreading OS:
- Online processing OS:
- Network Operating System:
- Real-time OS:
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- GUI interface is easy to operate and user-friendly.
- Users don't have to understand the syntax.
- An amusing environment can be created because of a friendly environment.
- Users don't have to remember all the commands.
- It requires larger space and faster processors to operate.
- GUI-based OS are usually 32-bit or 64-bit.
- It supports a multimedia environment.
- It is capable of operating multitasking, multi-programming, and multi-user systems.
Character User Interface (CUI)
- CUI is less user-friendly than GUI.
- Commands are used to instruct the computer.
- The user needs to remember the commands for operating this system.
- It cannot display graphics, icons, pictures, multimedia, etc.
- CUI-based OS are usually 8- or 16-bits OS.
- It is much faster than GUI-based systems.
- It is single-tasking and single-user OS.
- It does not support a multimedia environment.
- It can be used on low memory and low processing speed computers.
- Single User OS:
- Multi-user OS:
Concept of Open Source Software (OSS)
Open-source software (OSS) is any computer software that's distributed with its source code available for modification. That means it usually includes a license for programmers to change the software in any way they choose: They can fix bugs, improve functions, or adapt the software to suit their own needs.
Some common examples of open-source software are: OpenOffice, VLC media player, Mozilla Firefox, Linux, Android by Google, Apache (web server), etc.
Advantages of OSS:
- Cheaper than commercially marketed products.
- Created by skillful and talented people.
- Highly reliable due to more independent programmers testing and fixing bugs.
- It is more flexible and easier to build custom interface or add new abilities.
- Help achieving greater penetration of the market.
Disadvantages of OSS:
- Can Be Risky.
- It’s not User Friendly.
- Less Personalized/ technical Support.
- You need to pay sometimes.
UNIX:
Unix is a powerful, stable, multi-user, multitasking operating system developed at Bell Labs in 1969 by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie. It can be used in servers, desktops, and laptops or on a variety of platforms. It is available on both CUI and GUI format. It was one of the first operating systems developed in a high-level programming language, which allowed it to be easily ported between different hardware platforms.
Many organizations and companies developed their own system based on Unix implementation. For example, Apple’s Mac OS/X, GNU/Linux, IBM’s AIX, Solaris, IRIX, and FreeBSD.
There are both commercial such as Sun’s Solaris, IBM’s AIX, Mac OS/X, and non-commercial variants such as GNU/Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD.
Components of UNIX:
- The Kernel:
- Utility Programs:
- System Configuration Files:
- The Shell:
Features of UNIX:
- Multi-programming: Supports more than one program in memory at a time. It amounts to multiple user processes on the system at the same time.
- Multitasking: A user can also run multiple programs at the same time; hence Unix is a multitasking environment.
- Multi-user: Several people can use a Unix computer at the same time; hence Unix is called a multi-user system.
- Portability: It was one of the first operating systems developed in a high-level programming language, which allowed it to be easily ported between different hardware platforms. So, developers can develop suitable software for varieties of systems.
- Better system security: Security refers to preventing users from interfering with each other or data, programs. It provides security in several ways such as using username and password for logging in, working according to the permissions i.e. read/write files or stop programs.
- Supports Graphical User Interface (GUI).
- Supports both character user interface (CUI) and Graphical user interface (GUI).
Linux:
Linux is a free, open-source, UNIX-like operating system that has a wide following among developers and end users alike. Linux is similar to Unix in that it is a stable, multi-user, multitasking operating system that can be used as a server or desktop operating system.
Linux is very different from Windows. There is no "one" Linux operating system. Instead, Linux is developed by a number of independent developers and companies, with each contributing their own version of the operating system.
Linux comes in many different "distributions" or versions, but all share the same basic components. Some of the most popular Linux distributions are Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, CentOS, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Components of Linux:
- The Kernel:
- Shell:
- GUI:
- Utilities:
Advantages of Linux:
- Open-source: Linux is free and open-source, which means anyone can view, modify, or distribute its source code.
- Stability: Linux is known for its stability and reliability, making it a popular choice for servers and critical systems.
- Security: Linux has strong security features and is less vulnerable to malware and viruses compared to some other operating systems.
- Customizability: Users can customize Linux to suit their needs and preferences, thanks to its open nature.
- Community support: The Linux community is large and active, providing extensive documentation and support for users.
- Compatibility: Linux supports a wide range of hardware and software, making it versatile for various applications.
Disadvantages of Linux:
- Learning curve: Linux may have a steeper learning curve for users accustomed to other operating systems.
- Software availability: While Linux offers many open-source software options, some proprietary applications may not be available for Linux.
- Hardware drivers: Linux may require additional effort to find and install drivers for certain hardware components.
- Fragmentation: The variety of Linux distributions and desktop environments can lead to fragmentation, making it challenging to choose the right one.
Best Linux distributions
- Ubuntu
- Elementary OS
- Cent OS
- Linux Mint
- Open Source
- Arch Linux
- Fedora
A mobile operating system, also called a mobile OS, is an operating system that is specifically designed to run on mobile devices such as mobile phones, smartphones, PDAs, tablet and other handheld devices. The mobile operating system is the software platform on top of which other programs, called application programs, can run on mobile devices.
Some common examples of mobile operating system are: Android, iOS, KaiOS, Windows, Black Berry OS, etc.
Conclusion
Computer software and operating systems play a crucial role in the functionality and usability of modern computers. Understanding the different types of software and operating systems, their features, and their advantages and disadvantages is essential for computer users and professionals alike. Whether you're using a Windows PC, a Mac, a Linux machine, or any other device, having a basic knowledge of computer software and operating systems can help you make informed decisions and troubleshoot common issues.
As technology continues to evolve, the world of computer software and operating systems will also continue to change. New innovations and developments will shape the future of computing, and staying informed and adaptable will be key to navigating this ever-changing landscape.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *